
What makes thoughts spark inside your head? From memory to imagination, split-second choices happen without warning. One moment you recall a face, next you picture tomorrow. This hidden network shapes every move, yet remains largely unknown. Mystery wraps around its power like fog.
Though people swap "brain" and "mind" like spare change, they aren’t quite the same thing. Inside your head sits the brain - actual tissue, weight, shape. What you feel, remember, think, dream - that swirl comes from the brain but belongs to the mind. This piece walks through that inner world, poking at how thoughts rise, why feelings stick, what gives the mind its quiet strength.
Youtube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tOEKPYppWRI
Starting with the brain helps explain how thoughts form. Billions of tiny nerve units, known as neurons, build this organ. From one cell to another, messages travel using electric pulses along with chemicals.
Signals zip through intricate webs whenever thought, motion, or sensation strikes. In a flash - mere thousandths of a second - the message arrives.
One part of the brain tackles one job, while another deals with something else entirely. Take movement - certain zones run that show, yet feelings come from separate corners altogether. Memory? That lives in its own neighborhood, just like choices do, though they aren’t always neighbors.
What catches attention about thinking? It's built as brain cells connect, passing messages back and forth. These tiny exchanges spark each idea that forms inside us.
Seeing triggers one part of the mind to work. A different region jumps in when noise arrives. Because signals merge, sense emerges. Meaning forms where sight meets sound.
What you've lived through colors how you see things now. This explains why one event might hit two folks in completely different ways.
Inside your head, memory helps everything run. Information sticks when nerves link again and again. Repeat it, then those links grow tighter by far.
When fresh connections fire up in the brain, learning takes place. Because repetition builds those links stronger, remembering later becomes smoother. From that point on, each try shapes memory a little more.
Because the brain gets stronger when it learns a little each day, routine study builds both recall and clarity. How often you review shapes how well things stick.
Fueled by deeper currents beneath thought, feelings shape the way people respond. Different zones inside the head handle these shifts, guiding actions without words.
From time to time, a rush of joy, fear, or eagerness shifts what's happening inside. Brain chemicals shift gears, shaping thoughts along with physical reactions. These inner changes guide how you move, respond, even breathe. Signals travel fast, linking feeling to function without warning. Each emotion tweaks both mind and muscle in quiet but clear ways.
Faced with a choice, the mind first sifts through facts, lines up possibilities, then guesses what might happen next. Logic pulls one way, feelings another - somewhere in between, a decision takes shape.
Most thinking slips past awareness. Beneath the surface, much of the mind's work unfolds without being seen.
Beneath awareness, routines and reflexes run on their own. Hidden gears turn while attention looks elsewhere.
Funny how the mind handles familiar actions - walking, say, or cleaning teeth - without needing full attention. What feels automatic often skips conscious effort entirely. Routine slips into motion before thought catches up. Ever notice that? The body just moves through steps already learned. Attention wanders, yet things still get done. Because repetition trains behavior below awareness. Like breathing, almost. Happens whether watched or not.
Inside the skull, a network of countless nerve cells hums with quiet energy. Not just shaping feelings or ideas but also holding moments from long ago, it guides each move you make without pause. What seems like simple choices are actually built on layers of silent electrical storms firing beneath your forehead.
Beyond mere thought, the mind reveals layers of hidden ability. Through effort, repetition, one gains sharper clarity over time. Growth shows up quietly - shaped by routine choices, small efforts linked together. Focus deepens when nurtured slowly, without rush. Creativity grows not in leaps, but through steady doing.

 Feb 21, 2026
Feb 21, 2026

 Feb 21, 2026
Feb 21, 2026

 Feb 21, 2026
Feb 21, 2026
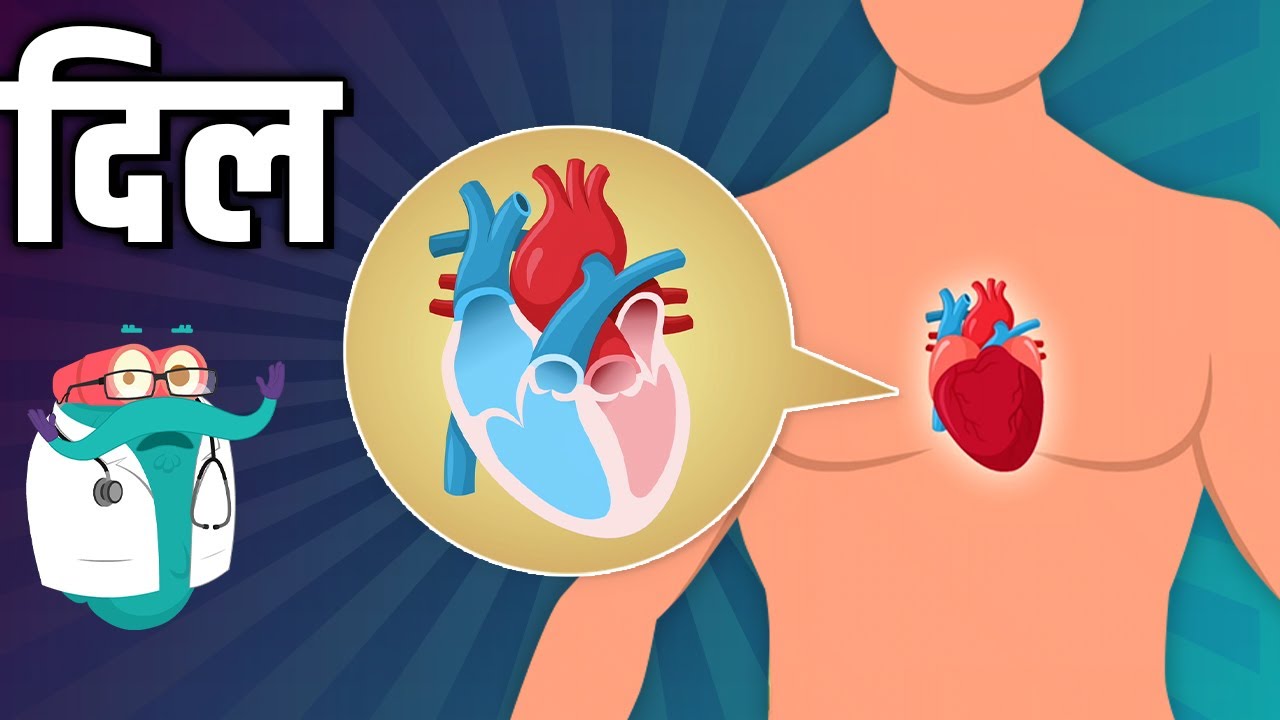
Every now and then, try pressing a palm just below your collarbone. What meets you there is a quiet pulse, constant like clockwork. This beat? It comes from the muscle shaping your breath, your movement, your being. Not flashy, yet running everything behind the scenes.
Every single moment, the human heart stays active. Without pause, without rest, it moves blood through your body. This vital organ simply does its job - constantly, quietly, endlessly.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i-c8CAYkVX8
Beneath the ribs sits a strong muscle, shaped roughly like a clenched hand. Off-center toward the left rests this vital pump, shielded naturally by curved bones above it.
Built for one task, yet crucial to how it works
Your heart moves liquid through every part by pushing it along.
Blood carries:
It is the heart that sends each one on its way. Without it, movement stops before it begins.
A strong beat keeps things moving through four separate spaces inside the chest. One chamber pushes first, then another follows right after. Three more join at different moments to keep the rhythm steady. Each part opens and closes like clockwork during every pulse
Here’s how the process works:
Every minute, the pattern loops anywhere from sixty to a hundred times in most grown-ups.
Inside your chest, a rhythm taps out each beat when valves seal off chambers. That steady lub-dub? It happens right after those flaps clamp closed.
Every single day, roughly one hundred thousand pulses move through your chest. When you look across years, those keep coming, never pausing, building into numbers too large to count.
When the heart works, it sends oxygen to your brain, your muscles, every organ. Without that flow for just a short time, harm begins fast.
When you move more, it pumps faster. Needs shift, so does its rhythm. As demands rise, output changes too. It follows your body’s cues without delay
When you move, it moves. Your effort shifts, it adjusts right away. As pressure builds, it eases without delay. Every change you make pulls a quiet reply.
Every beat counts when it comes to staying healthy. Staying active helps maintain strength inside your chest
A single choice today can shift how things feel later. Tiny steps pile up when done again and again. Doing just a little each day shapes what comes next. Repeating small actions slowly changes the whole picture. What seems minor now grows stronger with time.
Life hums because of a fist-sized pump working without pause. This muscle kicks into higher gear when you move, slows when you rest. Each thump pushes liquid fuel through hidden tunnels inside you. It does not stop, cannot quit, will not wait.
When your heart beats again, think of it - this tireless worker deep within, always moving, always there. A quiet force, built strong, doing its job without pause. Not flashy, just steady. Always keeping you going
Out of nowhere, the floor shifts while you're just resting inside. Walls shiver, things on shelves jump and clatter - balance vanishes in an instant. This jolt, brief but sharp, goes by another name: quake.
Shaking ground might feel tiny - or shift entire regions overnight. What makes the planet tremble like that? Here’s how it really works.
Youtube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OUlD5fkYN_4
Shaking happens when the ground moves suddenly because something shifts far below us. The outside part of our world looks whole but it actually cracks into big chunks. These pieces go by a name - tectonic plates - and they shift around without warning.
Far beneath our feet, chunks of Earth inch forward over long stretches of time. When one jolts into another without warning, force bursts loose. This surge rolls outward like ripples through solid rock. The surface trembles as those pulses pass by.
Earthquakes happen mostly because huge pieces of Earth shift. One kind of motion pushes plates apart. Another pulls them together. A third lets them slide past each other sideways
Shaking happens when trapped force between the plates escapes fast. Sometimes it's not steady - it bursts loose without warning. That sudden break makes everything tremble. Pressure that stayed locked gives way at last. Movement like that can’t stay hidden. The ground reacts each time. A shift deep down sends ripples outward. Energy waits, then runs free. What was still becomes motion in seconds. Tremors follow whenever tension snaps.
Out from the center, shaking begins when the ground splits open during a quake. Traveling through Earth, these ripples of force carry the jolt far away. Called seismic waves, they move fast beneath the surface.
Pulling apart rock deep below sets off quakes at a spot known as the focus. Right up from there, where things hit hardest, marks the epicenter. Closest to that surface point, tremors often feel most intense.
Beneath shaky ground, a device known as a seismograph records quakes. When tremors strike, their power shows up through numbers on the magnitude scale.
A quake gets more intense when its number goes up on the scale. Take this case:
Fault lines crack through places where giant slabs of Earth bump into each other. Around the Pacific, one well-known zone - called the Ring of Fire - heaves with constant tremors and fiery eruptions.
Shaking happens a lot in places such as Japan, Indonesia, or California - these spots sit right where Earth’s plates edge up against each other. Though quiet elsewhere, these zones crackle with constant underground shifts simply due to their position. When slabs grind slowly day after day, tremors follow without warning. Not every region feels it equally; only those straddling seams notice the deep rumbles regularly. Movement beneath the surface chooses its targets by location alone.
Hard to say when, yet scientists spot quake-prone zones using ground shifts. Still unclear on timing, experts track tectonic motion to sharpen alerts. Though patterns emerge, precision remains out of reach today. Watching plates creep helps refine how fast warnings go out. Location clues exist, even if moments stay unpredictable. Each tremor studied adds small gains to forecasting speed. Ground stress shows hints, just not full answers yet. Data piles up slowly, inching closer to timelier signals.
During an earthquake, remember:
Calmness during tough moments changes outcomes. Readiness shifts how things unfold when pressure rises.

Shaking ground shows how restless our world really is. Below the surface, giant pieces of crust never stop creeping. Usually, nothing feels different - yet once energy bursts free, everything trembles.
Felt the ground shake? That's nature reminding us how little we control. Forces deep below push and pull, making quakes happen when least expected. Staying ready means knowing what might come - without fear, just awareness. These tremors shape mountains, carve valleys, reveal Earth’s restless core. Respect grows when you see power beyond human scale at work.
Ever thought about why we stay stuck to the ground? After all, our planet is shaped like a ball. People live on the far side, completely flipped compared to us - yet they do not drop off into emptiness. Gravity pulls everything toward the center, no matter where you stand. That force keeps both them and us firmly in place. Direction depends on location, nothing more.
What if the secret isn’t magic but something unseen pulling everything together? This quiet pull shapes each moment, though most never notice its silent role in daily life.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rLxytS7fNHc
Down here on Earth, stuff moves toward the middle because of an invisible tug. This pull comes from a basic force found in nature - objects draw close without touching.
That means:
Firmly held down, we stay put thanks to that steady tug beneath our feet.
What catches attention next is how space doesn’t actually have a true up or down. Direction loses meaning when floating among stars.
A globe shape defines our planet, much like a sphere. Because of gravity, objects move inward, aimed at the core. Standing in India, or across in America, even way down in Australia, direction shifts quietly underfoot. Toward the middle of the world feels like down, wherever you are.
Down under, folks stand flat-footed without tipping over. Gravity tugs them straight down, same as it does for you. Their floor pulls just as hard as yours.
Earth’s gravity is strong enough to:
Even though it holds us, the force isn’t powerful enough to freeze our movement. When we leap upward, push forward, or toss an object into the air, something tugs us - and them - back again.
If gravity suddenly disappeared:
Few things matter more than the quiet forces shaping existence.
What holds everything in place isn’t only what keeps your feet on the ground - it binds the whole planet like an invisible thread.
A falling apple sparked it all, they say, back when Newton walked the earth in the 1600s. That moment under the tree shifted everything, not with noise but quiet thought. Instead of ignoring the fruit's drop, he wondered - what if that tug works beyond branches? Suddenly, the Moon wasn’t just hanging there; something unseen held it close. His mind linked orchard and orbit through one steady pull.
Suddenly, the way we saw gravity shifted when Albert Einstein stepped in. Heavy things warp both space and time around them - that was his idea. He showed it not as a pull but as a curve created by mass. His view stretched what came before, fitting better with how the universe behaves.

Downward pull comes from deep within Earth, holding everyone in place. Wherever a person stands, that grip never lets go - keeping things steady underfoot. Stability arrives without effort, simply by being here.
Every moment, without a sound, gravity works. Though unseen, it shapes how things move across space. Jump high, come down slow - something steady pulls you always. Each landing reminds us: this force never rests.
A flash slicing through dark skies - gone before you can blink. Some shout "shooting star," though stars have nothing to do with it. That quick blaze? A speck of ancient rock, vaporizing under speed and friction high above. It's not glowing; it's dying in fire miles up.
A flash in the sky might vanish fast, yet it brings secrets from far beyond our world.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0U-ja-ITlDw
To grasp what meteors are, start by learning three connected ideas:
A flash streaks across the sky - what people call a shooting star is really just a small space rock catching fire way up in the atmosphere.
Falling stars usually begin as bits left over when planets first took shape. Often, they’re pieces broken off from asteroids after collisions long ago
Now and then, our planet sweeps through leftover bits of rock and ice when orbiting the Sun. Those leftovers often come from comets that passed long ago. Bright streaks fill the night sky during these events. A sudden burst of falling stars marks what we call a meteor shower. They arrive on schedule each calendar cycle. Timing can be expected well ahead of arrival.
Faster than seventy kilometers each second, meteors streak through space. Hitting our atmosphere, they slam into bits of air. Heat builds up from rubbing against the sky, making the rock glow fierce. Bright trails mark where they’ve burned.
That bright line across the sky? It comes not only from the rock catching fire, yet from the air around it warming until it glows. Small bits - often as small as sand - still manage to light up the night with a sudden spark.
Falling stars often vanish high above Earth. Yet they paint the sky with fleeting light.
Still, some huge space rocks make it through the atmosphere, hitting Earth as meteorites. Uncommon though they are, such moments show how lively and busy outer space really is.
The best way to see meteors is to:
Curiosity matters most when the sky stays cloudless. What counts is looking up without needing tools nearby.

A flash tears across the night - sudden, brief, bright. These tiny travelers from deep space arrive without warning, glowing only a heartbeat before vanishing.
Next time a shooting star cuts across the sky, hold that thought - it is more than just a flash. A small fragment of space journey ends in fire right there, lighting up the dark with ancient travel logs.
One moment you're enjoying dessert, then - sharp pain hits. Sugar could be triggering that ache in your mouth. Holes in teeth often lead to these jolts of discomfort. Kids get them just as much as grown-ups do.
Still wondering about those holes in teeth? That’s where trouble begins. This piece explains their origin, uncovers reasons behind crumbling enamel, reveals everyday habits speeding up damage, shows ways to stay ahead of rot. Each detail here keeps gums strong, guards against slow breakdowns, supports lasting smiles without surprises.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xnPDV5YEsqU
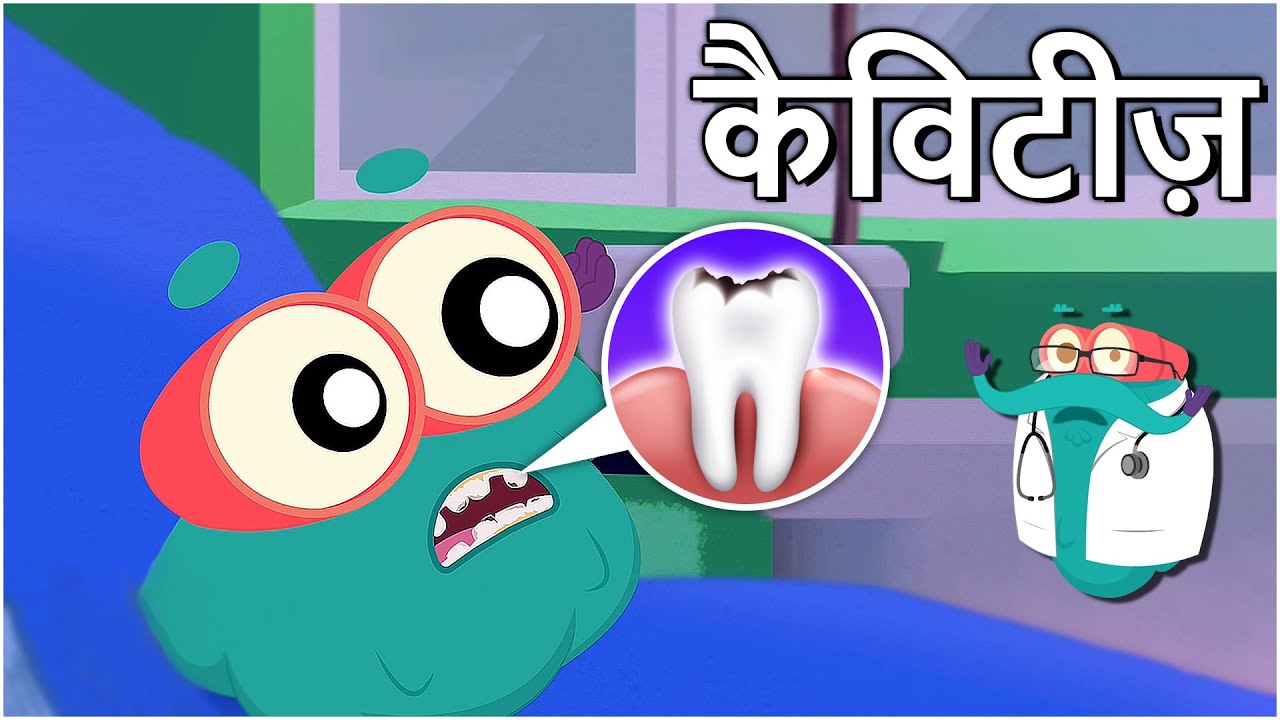
Built by acid-wielding microbes, tiny openings chew into the tough outer layer of teeth. These spots show up after germs linger, souring on sugars and softening protective shields.
That hard surface on your teeth? It’s called enamel. If acids soften it, tiny bits begin to chip away. Slowly, these small losses grow into holes.
Sugar-heavy treats like candy or soda give mouth bacteria something to thrive on. Most tooth decay comes from not brushing well enough while eating too many sweet things. Bacteria munch on leftover sugars after meals or snacking. Chocolate, desserts, or soft drinks leave traces that fuel harmful germs. Brushing too little lets those germs grow stronger every day.
Fueled by sugar, bacteria churn out acid. Over time, that acid eats away at enamel, sparking decay.
Bacteria cling to teeth when cleaning slips through the cracks. This gooey film sticks around if tooth care feels like an afterthought. Left unattended, tiny holes begin forming where enamel weakens. A steady routine keeps those spots from turning into trouble.
Sometimes at first, a cavity won’t show any clear signs. As damage grows inside the tooth, discomfort might start - especially when biting down, noticing dark spots, or feeling sudden twinges.
Foul odors from the mouth along with discolored patches might mean tooth decay is forming. Without care, those damaged areas grow worse, bringing intense discomfort or possibly spreading bacteria.
Most people avoid cavities by keeping up with their mouth routine. Each morning and night, a fluoride paste scrub cuts acid threats. Between those back teeth? String floss drags gunk out each evening. That simple move blocks sticky layers from growing.
Fewer sweets mean fewer chances for cavities to form. Rinsing the mouth with water once eating ends clears bits stuck behind.
Finding problems fast - that is what happens when visits happen often. Spotting trouble before it grows makes fixing it easier later on. Catching small issues keeps bigger ones away down the road.
Biting into food, forming words - teeth handle it all when they’re strong. When brushing slips, trouble creeps in beyond cavities. Gums turn sore, swell, sometimes bleed without warning. Body-wide shifts follow, quietly tied to that neglected rinse.
Fresh breath starts with brushing each morning, yet skipping it invites trouble down the road. A clean tongue plus flossing every night keeps gums firm, while sugar sneaks in unseen to feed decay. Shine shows when mirrors catch your grin; hurt hides until swelling won’t ignore.

Few tiny holes in teeth might seem harmless - yet they signal deeper trouble rooted in rot. As microbes feast on sweet bits left behind, acid brews slowly. This sharp liquid gnaws at the hard outer shell of a tooth, wearing it down.
Brushing well, cutting back on sweets - these steps help stop tooth decay before it starts. Seeing a dentist often makes a big difference over time. Small habits now build tougher teeth later. Your future self might just thank you when smiles stay pain free.
Most little ones mix up left and right at some point. Sometimes they cannot tell north from south either. Knowing how to find your way matters in daily life. This kind of awareness helps children make sense of space around them. Disha gyaan, or direction learning, fits into that need naturally.
Knowing which way is which - that is what disha gyann really stands for. Kids start making sense of where things are when they grasp direction. This piece looks into how little ones see space around them. Why pointing matters grows clear once you watch how they move through rooms. Fun games often sneak in lessons about left, right, up, down. Learning turns playful when clues hide in motion.
YouTube video link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gb2MJKI6Qi8
Disha gyaan is knowing which way places lie - north, south, east, or west. Called primary points on a compass, these guide basic orientation. Between them sit half-points: northeast sits between north and east, for example. Northwest hides where north fades into west. Southeast appears when you split space after east turns southward. Southwest forms opposite to northeast across the circle.
Out there, kids begin noticing corners and edges once they try guiding scenes. Movement makes sense slowly - how a step here leads past that shelf, why turning matters near the door. A chair isn’t just sitting anymore; it’s part of a path.
Figuring out which way is up or down builds a kid's sense of space. That sense? It’s really about how things sit near or far from one another.
Say a kid picks up how left and right work - suddenly, directions such as “Take a left at the corner” make more sense. Because of that, they start making better sense of maps, even grasping basic geography without much effort.
Disha Gyaan plants quiet strength. When a kid grasps which way is north, they move through familiar spots - bedroom, classroom, slide area - without holding someone's hand.
Start with games that move like stories. A child might learn disha gyaan without even knowing it. Jump into directions by playing classroom compass tag. This way, lessons feel more like playtime. Try using colorful maps drawn on the floor. Watch how easily pointing becomes understanding. Another idea hides clues around a yard. Each step follows east, west, north, or south. Learning sneaks in through laughter. Even a song about left and right helps build awareness. Surprise them with a blindfold walk guided only by words. Moments like these stick longer than drills. The key is mixing motion with meaning.
Picture this: a child watching sunrise. The light spills over the land each morning from one side of the sky - east. By day's end, that same glow slips away in the opposite direction - west. Knowing where the Sun appears helps kids mark their path without confusion. Their minds begin linking warmth and daylight to those edges of the world.
A game of hidden surprises can spark joy. Follow hints such as “walk three steps forward toward the northern edge” or “head in the direction of the eastern wall.” Learning feels alive when it moves with you.
A child might get the hang of direction by sketching a quick layout of rooms. Or maybe using a compass makes it click - seeing which way things point inside their home.
Left, right, behind - these words show up everywhere. Not only on signs but also at home. Imagine pointing toward a room while speaking. That moment uses what you know about position. Even simple phrases like “next to the tree” rely on it. Wayfinding happens all day without us noticing.
When kids learn disha gyann, getting around safely starts making sense. Growing up, riding bikes or crossing streets feels easier because of it.
A child might just need someone pointing the way, which we sometimes call disha gyaan. This kind of guidance builds awareness about where they are. Following directions becomes easier when it feels natural. Confidence grows quietly through such small moments.
Games turn direction lessons into something kids actually enjoy. Real moments matter more than textbooks when showing left from right. Simple words help small minds catch on fast. Adults guide without making it feel like school. Knowing which way is north builds confidence slowly. The world feels bigger once a child finds their way. Independence grows quietly through practice. Awareness sneaks in while they’re busy playing.
Curious how we learn about creatures from long before humans? Clues come from stone shapes where bones once were. These hardened remains act like messages from deep time. They let us piece together who lived, how they moved, what they ate.
Fossils tell stories from long ago, hidden inside rocks. How these ancient remains come to exist involves slow changes over immense time. One kind might be a shell trapped in stone, another could be just an imprint left behind. Because of them, researchers piece together Earth's past life bit by bit. Their value shows up in labs, classrooms, and quiet discoveries.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QE5OJIOmI8A
Frozen in stone, fossils show what's left of ancient life forms from ages past. Often buried within layers of rock, they might have taken countless millennia to form.
Frozen in stone, bones or teeth might last millions of years. Footprints pressed into mud long ago sometimes harden just like shells do. Leaf marks on rock tell quiet stories of forests gone. What remains gives clues about creatures no one sees alive now. These traces sketch out worlds that once thrived but vanished.
Dead plants or creatures normally vanish - broken down by microbes or gobbled up fast. Burial beneath layers of silt, though, changes everything. Only when mud swallows them just right does the slow road to stone begin.
Frozen moments pile higher, pressing weight onto what's left below. Water slips through, carrying minerals that swap out soft tissue bit by bit. Slow shifts turn bone and fiber into something hard, like rock shaped from memory. What was once alive now rests in silent form.
Fossils form when remains get trapped in layers that slowly harden into stone over vast stretches of time.
Preserved remains take shape in many ways, each revealing a piece of ancient life. How something turns to stone depends on the conditions it meets underground. Some leave imprints while others slowly replace bone with minerals. Trapped shells harden differently than footprints filled with sediment. Each process tells its own story through time's slow press.
Parts of creatures such as teeth or bones often survive as body fossils, a typical example found in rock layers.
Footsteps stuck in stone tell a story too. Trails left by creatures long gone give clues about how they moved. Marks dug into ancient mud still show where life once stirred. Dung turned to rock also counts as one kind of these traces.
A shape left behind by a creature can harden into stone over time. When that hollow outline gets packed with minerals much later, it turns solid again in new form. The first stage holds only space where life once pressed. What fills it afterward becomes a copy shaped by chance.
Frozen remains give clues about ancient creatures, revealing shifts across ages. Because of these buried traces, researchers trace how living things transformed through eras.
Pieces of old life hide hints about how nature used to be. Take ocean creatures turned up in dry places - they tell a tale of flooded lands long ago.
Fossils reveal what life looked like long ago; without them, we’d know little about past creatures. Hidden traces in rock tell stories bones alone never could.
Frozen moments in stone whisper stories of long-gone creatures. Through them, we piece together vanished worlds, one bone at a time.
Look again at that dinosaur frame in the glass case - stone holds ages of stories, stacked slow beneath ground. These bones peek through deep time, showing pieces of an ancient world we can almost touch.
A whirl of wind twists over fields, loud and wild - that fierce sight has a name. Tornado. What even is one though? How does something so strong begin out of nowhere? A spin builds where air moves differently, cool meets warm, chaos takes shape.
A sudden twist of wind builds where storms collide. This piece looks at nature's violent spirals - how they start, why they spin, what feeds their power, yet leaves ruin behind. Wild air takes shape when heat meets cold above open land. Rotation begins inside clouds before touching ground.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S84NvY0DAl8
Spinning wildly, a tornado reaches from storm clouds all the way to earth below. Not always visible at first, the twisting wind often takes shape like a narrow cone hanging from above. Wherever it moves across terrain, destruction tends to follow close behind.
Spinning like a top, tornadoes earn the nickname twisters from their wild rotation. Hurtling forward, wind inside them hits more than 300 kilometers each hour at peak strength. Trees snap loose when hit by such force, structures crumble without warning, cars get tossed as if weightless.
A spinning column of air reaches down from the sky when certain storms grow intense. These violent funnels often take shape inside massive thunderstorms known as supercells.
A pocket of humid warmth rising from the surface bumps into drier, cooler air up high, shaking up the balance in the sky. Swirling motion begins when winds shift pace and turn sideways as they climb, thanks to uneven flow across layers.
When the storm gets stronger, upward-moving heat lifts spinning air upright. Should that spin get faster and more focused, it might stretch down like a funnel, reaching for the earth.
Faster rotation kicks in when air races toward the middle. What drives that rush is lower pressure right at the core. Spinning starts thanks to uneven push across the sky. Motion grows wilder near the heart of the swirl.
A twist like water circling a drain shows up here too. Wind gets faster as the funnel tightens.
Tornadoes show up in various places across the globe, yet some areas see them more often. Across the U.S., a stretch called Tornado Alley faces regular twisters due to just-right storm setups.
Tornadoes aren’t just limited to one region - wherever clashing warm and cold winds meet, they might spin up. Sometimes it’s the heat that pushes forward, meeting icy fronts sweeping down. These collisions create chaos in the sky, twisting air into funnels without warning. Not every place sees them often, but when conditions align, nature doesn’t care about borders.
A whirlwind's strength lies in fierce gusts, also its route often shifts without warning. Speed matters when these storms appear out of nowhere, sometimes veering left then right in minutes.
When a tornado hits, pieces of broken objects fly through the air - these can hurt people or break things. Because of that risk, alerts and prepared steps matter most where twisters happen often.
A whirlwind begins like this: swirling air, strong enough to twist trees and rip roofs apart. This force grows inside fierce storms, where wind spirals upward fast - sudden, loud, impossible to ignore.
Spinning air isn’t just chaos - it follows rules hidden in storm clouds. When wind shifts high up meet warm rising air below, something twists loose. Safety grows stronger when people pay attention before sirens start. Warnings mean more once you’ve seen how fast calm turns wild. Nature shows force not to scare but because it must move that way.
Ever notice how most things out in space are always turning? Earth turns around an invisible line through its center. Planets move in loops around the Sun, while the Sun also twists like a top. Galaxies do it too, swirling slowly across time. That constant motion leads to one big question on everyone's mind: what causes all of this spinning across the cosmos?
Spinning happens because of how things move when pulled by gravity. This piece looks at why stuff out there keeps turning, what gets it going in the first place, yet never seems to stop. Motion starts small, then builds without anything to slow it down. Forces act long before light reaches us. Rotation sticks around simply since nothing stops it. Billions of years pass, still they whirl.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h6giolRdCYE
Spinning things everywhere? Blame the start. Clouds - huge ones made of gas and dust - become stars, then planets, say researchers.
Pulling inward by gravity makes the cloud shrink. During shrinking, any small motion already there sets things spinning slowly. Spinning grows stronger simply due to how rotation works in nature. The rule behind it holds turning speed steady when mass moves closer. Rotation stays present once begun.
Spinning things just keep going, unless something gets in the way. Out where there’s almost no drag, rotation carries on - sometimes for ages.
A newborn star gathers in the middle while leftover pieces settle into circles around it. Since that first swirling mass had motion, its fragments carry on turning.
Spinning like a top, Earth turns on its tilt while circling the Sun just like its planetary neighbors. Born from that swirling mass long ago, the Sun keeps turning too.
Spinning shows up everywhere in our cosmic neighborhood - because things just keep turning. Motion sticks once it starts out there among planets and stars.
Out there, things work just like smaller systems but way bigger. Stars by the billion pack galaxies, along with gas and specks of cosmic dust. Spinning slowly, vast clumps of stuff gave birth to these spinning islands long ago.
Spinning started when gravity drew things inward. Around their cores, galaxies such as the Milky Way turn now, dragging stars and worlds through space.
Things slow down on our planet since surfaces rub against each other. Out among the stars, though, nearly nothing gets in the way to steal motion.
A planet, star, or galaxy that begins to spin keeps going - billions of years pass without stopping. With nothing really slowing it down, the turning just goes on, nearly forever.
Faster spin means shorter days across worlds far beyond our own. Because Earth turns, sunlight shifts slowly from one side to the other. Planets moving along curved paths stay balanced by gravity instead of flying off. Their tilted rolls through space tilt the sun's angle, making weather shift with time.
Spinning galaxies shape where stars end up. Because they turn, things stay steady out there.

What makes things whirl across space? Gravity pulls stuff together while spin sticks around. As giant gas piles shrink, any tiny twist grows stronger. With nothing much to slow them down out there, those turns just keep going. Motion never really stops once it starts.
Spinning begins small, then grows large - motion built into existence itself. When Earth turns under you later today, consider: this movement connects to something wider, older, flowing through space without pause.
One moment you’re walking outside, then - wham - a gust hits hard enough to make you lean forward. Air in motion isn’t just something that messes up your hair; people have learned to catch it, slow it down using big spinning blades. Those turning arms connect to machines underground, generating power quietly. Instead of burning things, we let nature push electrons through wires. Motion becomes juice without smoke.
Out there, spinning high above fields and coastlines, machines catch air in motion. These turn breezes into electricity without burning anything at all. Picture blades moving because wind pushes them - that movement powers homes. From hillsides to offshore spots, this kind of energy grows faster than most others. What makes it stand out is how little harm it causes nature. We take a close look here at what happens inside those tall structures. The way they capture flow matters more now than ever before. Power drawn from gusts helps us rely less on old methods. Future needs mean smarter choices start today.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7w6Qj0iDVHE
Air in motion gives us power we can use. When sunlight warms some spots on Earth more than others, it sets things in motion. Because of these temperature differences, air flows from places where pressure runs high toward zones where it drops low - this flow becomes wind.
Besides spinning blades, airflow holds power within its motion. Because of rotating parts inside, machines transform that movement into electricity instead of wasting it. With nothing more than this principle, people harness breezes across open fields.
Wind energy makes more sense once you see how turbines work. Standing high, these machines catch air movement with long arms spinning around a center point.
Blades catch the wind's push, starting rotation. Spinning begins when air moves across their surface. A shaft links to those turning blades, transferring motion. Connected inside, a generator waits for that movement. Mechanical force becomes electric current through its workings.
Far across flat lands, spinning blades feed energy into wires that run toward towns. Where breezes blow steady and wide, clusters of towers rise together on clear horizons.
Fueled by sunlight warming our planet, wind keeps moving without ever depleting. So long as daylight touches Earth, this flow won’t quit.
Running on wind means nothing toxic escapes into the sky. Fossil fuels pump out carbon and dirty air - wind doesn’t play that game. Less harm to nature adds up when the power flows clean. Slowing climate shifts becomes possible without burning things down.
A different plus? After setup, wind turbines run cheaper than regular power stations. Maintenance doesn’t eat up cash like older systems tend to do.
Besides its advantages, wind power faces certain hurdles. Since the breeze isn’t always blowing, output of electricity sometimes drops.
Farms of spinning blades across open fields sometimes push animals out of their homes when placed without care. Still, smarter designs now ease the strain on nature nearby.
Wind power steps into the spotlight as global interest grows in greener options. Instead of leaning on coal or oil, many regions now turn to spinning turbines across open fields. Clean air follows where blades spin above hillsides and shorelines.
Farms of spinning turbines rise across nations chasing cleaner power for rising demand. Wind energy now fills sockets where fossil fuels once dominated daily supply. Across open plains and coastal edges machines turn air into current quietly.

Spinning high above fields, wind turbines turn breezes into power. Because nothing burns, the air stays clear when generators run on gusts instead.
When you spot those tall turbines out past the fields, know they’re pulling electricity right from the breeze. Each spin feeds homes without burning anything at all. Quiet machines doing real work while we go on with our days.
Bones - those hidden parts inside you - are why you stand tall every day. What might surprise you is how they do more than just hold things up. Without them showing, they shield delicate pieces deep within. Shape comes from these quiet workers beneath the skin.
Bones might seem quiet, yet they’re always busy inside your body. What if you knew each one plays a role far beyond just holding shape. Their job includes making blood cells, storing minerals, even helping movement happen smoothly. Without strong bones, daily actions become harder than expected. Eating well matters, but so does moving often in ways that surprise them. Keeping them working well means thinking ahead, starting now.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kc-5LF8zW_I
Built tough, bones shape the body's inner frame. A full-grown person carries exactly 206 of them. This network holds up muscles, organs, and all surrounding tissue.
Bones might look still, yet they’re full of life. Made of cells along with collagen and minerals such as calcium or phosphorus, they work quietly beneath the surface. Toughness meets a hint of give thanks to that mix.
Standing upright happens because of bones. They give form, hold everything together. Movement needs their support. Shape comes from them. Life without such framework? Hard to imagine.
Bones act like shields for key body parts. Take the skull - it wraps around the brain, keeping it safe. The ribs form a cage that guards both heart and lungs. Running down your back, the spine holds the delicate cord inside its bony tunnel.
Bones play a part in how we move. Connected to muscles, they get tugged whenever those muscles tighten. Motion happens because of that pull. Each tug shifts the bone slightly, allowing actions.
Bone marrow, tucked within bones, crafts blood cells vital for oxygen transport. Without it, infection defense would falter. The body relies on this inner sponge-like material just as much as the hard shell around it.
Some bones stretch out long, such as the one running down your thigh. These help you move when walking or jumping. Found in places like the hand and foot, others stay small and blocky. Their job is holding things steady without shifting too much.
Bones shaped flat guard soft parts inside you, think skull or ribs. Twisted forms stand apart - vertebrae fit here - built odd for special jobs. Balance and movement depend on what each one does, no two exactly alike.
Bones that stay strong matter more than most people think. Getting enough calcium through food makes a difference, especially when paired with vitamin D from sunlit moments outside. Dairy like milk and yogurt counts, sure - though kale and spinach do their part just as quietly. Sunlight on skin? That tiny daily dose plays its role without making noise.
Walking or jumping keeps bones sturdy when done often. Strong skeletons stick around longer if meals include real food instead of endless snacks. Heavy impacts from movement build density over time. What you eat matters just as much as how you move.

Built tough, bones hold up everything we do. Movement depends on them, while vital organs stay shielded underneath. Blood cell creation happens inside their core. Realizing what they do changes how we treat them.
Bones help without making noise each step you take, during runs, even when lifting heavy things. A steady routine of care keeps them ready for years of movement.
Curious about where plastic bottles go once they land in a recycle container? Lots of folks agree it matters, yet only a handful really grasp how factories handle the job. A journey begins at that blue bin - steps unfold behind closed doors, far from daily sight.
Every time someone tosses a plastic bottle into a bin instead of a landfill, less gunk ends up in rivers. Factories start by sorting what comes in - different colors, types, shapes - all pulled apart by hand or machine. Once grouped, the pieces get washed like dirty dishes, scrubbed free of labels, glue, leftovers. Water rinses away grime; machines spin out moisture till everything feels nearly dry. Heat melts each batch later, turning solid chunks into thick liquid streams. That goo gets pushed through tiny holes, forming wiggling worms that cool fast and snap into pellets. Trucks haul those beads to workshops where fresh items take shape - chairs, pipes, fabric, whatever fits demand. Each round skips raw materials usually dug from deep underground. Old wrappers become garden benches without burning extra fuel just to begin.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lPAG0l2_DgM
Starting at your doorstep, plastic waste gets gathered up - bottles, boxes, wrappers - all tossed into bins instead of landfills. From kitchens to workplaces, these bits travel through trucks and sorting hubs before anything else happens.
After arriving at the facility, the plastic gets divided by kind. Since each material behaves differently, separation matters a lot. Workers alongside automated systems group pieces according to shade, composition, and how thick they are. When done right, this step leads to cleaner recyclable output.
Once sorted, plastic gets washed to clear away gunk. Dirt vanishes along with sticky labels when water rushes through. Glue softens, food scraps fall off during the rinse cycle.
Water rinses plastics at the facility, occasionally aided by specific cleansing agents. Without proper washing, leftover debris might weaken the final recycled material's consistency.
After cleaning, giant shredders start breaking down the plastic. From there, it gets sliced into tiny bits known as flakes.
Fragments of plastic come out even, helping things move faster down the line. Melting gets simpler once the pieces are broken down first.
Melted down under intense heat, the plastic flakes enter their next phase inside the factory. High temperatures transform them into a flowing state during this step of recycling.
Out comes the molten plastic, sliding into a device named an extruder. Shaped by heat and pressure, it becomes long, thin threads. Cooling happens next - suddenly brittle, they snap into tiny beads. People call these bits recycled plastic ready for reuse.
Now comes the part where old plastic turns into something fresh. From tiny beads made of reused materials, everyday items begin to form. Bottles take shape under heat and pressure. Containers emerge through careful shaping processes. Furniture gets built using these durable bits. Pipes grow long and strong from melted-down pieces. Even threads for clothes come spinning out of this system.
This marks the end of how plastic gets recycled. What used to be thrown away now takes on a new role. A fresh life begins where trash once sat unused.
When plastic gets recycled, fewer trash piles build up in dumps or drift into seas. Because of that, trees, oil, and water stay out of the production line a little longer.
When old plastic gets turned into new items, it usually takes less power than starting from scratch. Because of that, fewer greenhouse gases go into the air, which does good for nature.

Waste arrives at the facility, already grouped by type. After that, machines pull out contaminants so only clean material moves forward. One by one, batches get shredded into tiny pieces under heavy rollers. These fragments travel along belts toward heated chambers. Inside, heat reshapes them into soft globs ready for molds. Suddenly, new forms begin to take shape - durable items meant for daily use. Step after step, old trash becomes something useful again.
A single choice can start a whole journey - tossing that plastic bottle into recycling could give it a second life. Later on, someone might hold what used to be yours in their hands without ever knowing the story behind it.
Imagine turning your regular bike into one that moves without pedaling. A small idea, really - swap in a 12 volt DC motor, add parts as you go. Some folks start by tinkering after work, others on quiet weekends. The trick lies not in skill but in trying. Tools help, sure - but curiosity pushes further. One piece fits next to another, then suddenly it rolls under its own power. Not magic, just motion made real.
A bike that runs on electricity doesn’t pollute, saves money, yet feels like a joy to use. This article walks through building one with a 12-volt DC motor - what you’ll need shows up next, followed by clear stages of assembly laid out step by step.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tSbZjhe28RI
First up, collect what it takes to build your e-bike. Key pieces? Think motor, battery, controller - those show up early. One thing leads to another once you have the frame ready. After that comes wiring, which ties things together without glue or tape. Wheels matter just as much when power gets involved. A throttle often joins the setup, though some skip it. Brakes change slightly because speed asks more from stopping. Tools appear along the way, not all at once. Each part has its moment before everything clicks
Electricity turns into movement through these parts, making the bike go even when you do not push the pedals.
Starting off, pick a motor that fits your bike well when making an electric cycle with a 12 volt DC setup. Weight matters - yours plus the bike’s - so the motor must deliver strong turning power.
A stronger DC motor, usually around 250W up to 350W, tends to fit small e-bike builds well. Connection matters - check that the motor's shaft lines up smoothly with your bike’s drive setup.
A small bracket often holds the motor in place along the bike’s back section. Usually, riders pick a spot close to the rear tire for mounting.
Brackets made of sturdy metal hold the motor tight. Since bumps while moving might shake loose parts, solid mounting matters a lot.
Power moves from motor to wheel through a drive setup. One option uses sprockets linked by a chain. Another picks belts instead of chains for the job.
Starting straight, the front chain gear must line up just right with the back one so turning stays fluid. When both gears match position, less resistance builds up, making motion easier. Smooth movement happens only if spacing is accurate across the system.
From the beginning, power flows when the 12-volt battery connects to the motor that runs on direct current. Placement matters - fix the battery onto the frame where weight spreads evenly across.
Starting at the battery, route power through a small box that manages how fast the motor runs. This device sits right between the energy source and the spinning part. Twisting your hand on the bar changes how much juice flows. Control comes alive when the throttle links into place up front.
Start by looking over every wire and connection - make sure each bolt is snug. Moving ahead, take it slow when testing the power bike.
Check that cords have good covering while brake systems respond well. Putting safety first matters most during homemade e-bike assembly. What you build needs to protect you above all else.
Home-built e-bikes with a 12-volt DC motor cost less, help the planet too. Fuel bills drop while pollution shrinks at the same time. Tinkering with one opens doors to understanding how motors work, along with hands-on engineering basics.
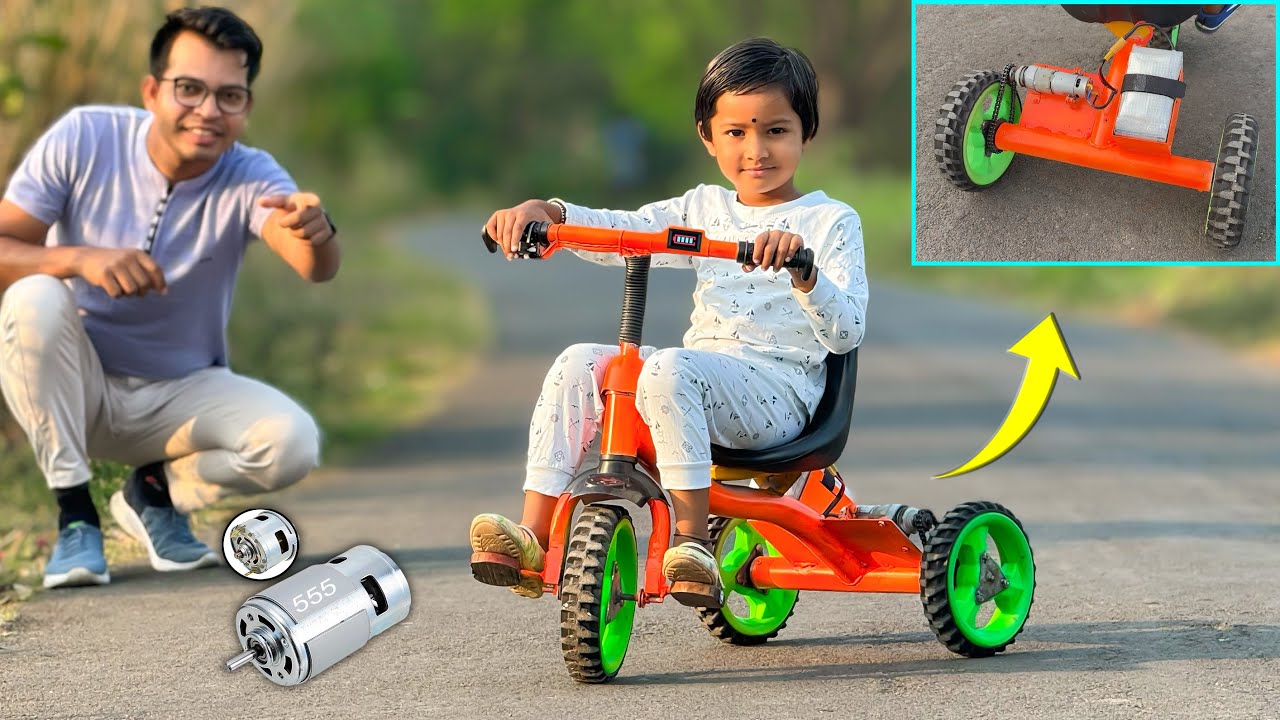

A fun way to learn? Try building an e-bike with a 12 volt DC motor. Using the correct parts, secure attachment methods, along with careful electrical connections, turns any standard bike into one that runs on power.
A homemade e-bike teaches real skills while helping the planet at the same time. Built with care, this ride turns into a practical choice that lasts.
What if your home made power just by sitting in the sun? A solar house pulls off this trick every single day. Costs climb, skies change - so folks turn to rooftop panels more often now. Sunlight becomes watts without smoke, noise, or fuel runs.
A solar home captures sunlight to make electricity, while heating water too in some cases. This piece explains how such homes operate, what they actually are, along with reasons behind their rising global appeal.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qA0Vax63tTQ
A solar house runs on power made by capturing sunshine through special panels. Sitting atop the roof, these units soak up light best when placed high and clear. Most of them work strongest under open skies with nothing blocking their view of the sun.
A solar home aims to cut back on power drawn from fossil fuels such as coal or natural gas. Relying on sunlight changes how energy needs are met, shifting away from outdated systems. Bills drop when rooftops collect rays instead of plugging into old grids. Cleaner air follows because sunshine leaves nothing behind but light.
When sunlight hits the roof, that is when solar panels come into play. Built using photovoltaic cells, these panels do their job without noise or moving parts. Sunlight gets soaked up, then turned into electric power through those small units inside. The energy created comes out as direct current, ready for what comes next.
Electricity moves through a gadget known as an inverter because household items mostly run on alternating current. This gadget changes direct current into alternating current, making it usable for things like fridges, bulbs, or ceiling fans.
Battery setups sit inside certain homes powered by sunlight. When daylight hours generate surplus electricity, that supply gets saved away. Nighttime needs pull from those reserves instead of outside sources. Cloudy stretches work much the same way - stored juice fills gaps left by weak sun.
A solar home can save money in the long run. Even though setting up panels means spending at first, many people pay less on power each month after that.
Besides saving money, going solar shields nature too. Clean power pours in when sunlight hits panels instead of smoke pouring out. Fossil fuels cough up fumes - solar stays silent, leaving skies clearer. Less gunk in the air means a cooler planet, breathing easier each day.
With solar homes, people lean less on outside electricity. When blackouts strike, they stay powered more easily.
One thing about solar homes - they come with perks, yet hurdles too. Paying for setup at first might stretch budgets. Sunlight levels change how well panels work.
Beyond better tech, rising support from governments helps bring solar power within reach of more households. Still, it's not just about lower costs - easier access plays a big role too.

Home powered by sunlight points toward how people might live smarter. Thanks to panels on the roof, cutting bills happens while nature gets a break. Less need for old energy systems shows up when sunshine does the work.
Sunlight now fuels homes more than ever, as rooftops catch rays instead of just rain. When you spot those dark glassy panels overhead, know they’re busy making electricity without smoke or noise. Step by step, these quiet systems help shift how we live - cleaner, simpler, closer to nature’s rhythm.
Up there, where clouds drift, something big moves through the air - planes. Heavy metal bodies rising without effort, crossing continents while floating above weather and time zones. Wonder sparks when eyes follow their path. Though grounded, people still question how such weight stays aloft. Magic isn’t real, but flight comes close.
Truth is, flying works because of basic physics. This post breaks down how planes create lift using their wings and engines while balancing four key forces needed for flight.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u2CnQBNgHWU
Lift, weight, thrust, and drag - those are what control flight. One doesn’t act alone; each balances another during travel through sky. Motion begins when engines push forward, while wings shape airflow above and below. Gravity pulls down just as lift pushes up, creating constant tug between earth and machine.
Upward push? That comes from lift. What lifts the plane skyward begins right at the wings. Motion through air sets it off, mostly thanks to how those wings are shaped.
Downward motion comes from gravity, which acts on the plane at all times. This pull, also called weight, keeps the aircraft drawn toward the ground.
Forward motion comes from thrust. That push moving the aircraft ahead stems from its engines. Without it, the plane stays still.
Slowing things? That's what drag does. Air pushing back while the plane goes ahead - that’s drag at work.
Lift needs to beat gravity so a plane can rise, while thrust pushes it forward by winning against air resistance.
Planes stay up because of their wings. On top, the wing curves in a special way. That curve has a name - airfoil.
Forward motion of the plane pushes air across the wing's upper and lower surfaces. The curve up top makes airflow speed up there, while beneath, it lags behind. With speed comes thin pressure on the outer side; down low, sluggish flow builds thicker pressure. That gap between high and low zones lifts the aircraft upward.
A push from uneven pressure moves the wing up, making lift happen. Once that upward force beats weight pulling down, the plane leaves the ground.
Forward motion begins when engines create thrust. Most big planes rely on jets that pull in air, squeeze it tight, then blend it with fuel before setting it alight. Out the rear, burning gas escapes fast, forcing the aircraft ahead. This push keeps going as long as the engine runs.
Faster movement pushes more airflow across the wings, boosting lift. That upward force lifts the plane and keeps it flying steady.
Up above, the pilot steers by adjusting parts built into the wings and back of the craft. With those pieces, moving up or down happens, along with changing direction.
Lift holds it up while gravity pulls down, yet steady flight happens when these forces stay matched. Thrust pushes forward; drag works against it, but motion stays even if they balance out. So long as none of those overpower, the aircraft keeps moving through the air without disruption.

Birds inspired early dreams of flight, yet machines took a different path. Lift pushes up when air moves faster above the wing than below. Gravity pulls down constantly, working against that upward push. Engines kick air backward, producing forward motion through reaction. Drag sneaks in, resisting speed whenever airflow catches edges. Design shapes each curve to handle pressure shifts without tipping the scale.
Floating up there, that plane isn’t pulled by dreams but held aloft by careful design. Behind its flight lies physics shaped by human thought, joined through quiet precision.
Ever stare into the evening sky only to find almost no stars? Darkness fades in numerous urban areas. Glare climbs upward now, fed by lamps on streets, lit windows, vehicle beams. Skyglow replaces blackness - human-made brightness taking over. Scientists name this effect: light pollution.
What if skyglow changes more than just star visibility? Human rhythms shift under artificial nights. Creatures navigate oddly when cities glow too bright. This piece explores sources of excess outdoor lighting. Disrupted sleep links to constant brightness overhead. Solutions appear simpler than expected - dimming helps. Seeing darkness return matters for ecosystems. Even small fixes alter neighborhood patterns. Nightscapes once familiar fade behind glare. Adjusting fixtures redirects wasted beams earthward. Quiet steps make night visible again.
YouTube video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hImB5ig5iPk
Dark skies vanish where city lights spill beyond their purpose. Overdone illumination from streetlamps, signs, or buildings floods upward instead of shining down. This glow lingers overhead because fixtures lack shields or operate through the night without reason. Brightness meant for safety often spreads where it isn’t needed.
Bright skies above cities come from scattered artificial light, known as skyglow. Instead of clear darkness, urban nights glow softly at the horizon because of it. Too much intensity in lighting creates glare, making it hard to see comfortably. This harshness often bothers eyes, especially around streetlights or signs. When beams cross into places they are not wanted, like bedroom windows, that is light trespass. Clutter shows up where too many lights crowd an area, confusing more than helping. Each kind disrupts natural night patterns in its own way.
Most light pollution comes from what people do every day. Because of streetlights, plus signs on stores, big work buildings, shops that stay open late, or lights at home, the night sky gets brighter.
Few realize how often bulbs glow through darkness long after purpose fades. Where fixtures lack proper covers, brightness escapes - climbing past rooftops rather than staying grounded on paths below.
Fewer stars become visible when urban areas spread, since more lamps brighten the night sky. Light spills upward where it is not needed, washing out darkness across neighborhoods. Bright streets stretch farther each year, replacing shadowed spaces with constant glow. Nighttime feels less like night as fixtures multiply on roads and buildings. Skyglow builds slowly, hidden in plain sight above rooftops.
Not only does light pollution hide the night sky, it messes with how nature runs. Animals that rely on dark might lose their way or struggle to eat and breed. Darkness guides many creatures, like moths flying toward nothing but stars. Take baby sea turtles - they follow the glow of the moon over water. When streetlights or buildings shine too bright, they crawl inland instead. Wrong turns often mean danger.
Bright nights take a toll on people too. When darkness should signal rest, artificial glow tricks the body’s internal clock instead. Sleep suffers when rhythms get thrown off track. Health often follows where sleep leads.
Wasted energy slips into the night through glowing streets. When lights stay on without reason, power gets used up - adding strain on nature’s balance.
Cooler nights start when we rethink how lights shine above. A shift to shielded LEDs cuts the glow that climbs into the sky. Lights that switch on only when someone's near make a difference too. Unplugging what isn’t needed trims waste without slowing life down.
Brighter nights don’t have to mean wasted light - cities might dim their lamps when streets empty. When adjustments happen slowly, stars begin reappearing overhead instead of vanishing behind glare.

Out there beyond city windows, too much brightness spills into the night sky. Though lights help people see after dark, they sometimes do more wrong than good. Glare pouring upward changes how animals behave during evening hours. Instead of helping, some lamps blind rather than guide. Nighttime creatures get confused by constant glow where darkness should be. Humans also feel effects without even noticing them.
Darkness matters when the lights go out. Each star above waits behind artificial glow. Wise choices about lighting shift outcomes slowly. Saving sky views ties to using less power. Healthier nights come through simpler habits. Think of shadows as necessary now and then. Brightness should not always win. Stars remain only if people care differently.
What if your closest buddy had wires instead of hair? One that checks math problems, joins hide-and-seek, yet also notices when your voice drops quiet. That’s where Chinki ends up - drawn into moments mixing wonder, small mistakes, and something like trust.
One day, Chinki stumbled upon a small robot near an old park bench. It wasn’t shiny or loud - just blinking quietly under the tree shade. She paused because it looked sad somehow, even without a face. Over weeks, they began meeting there each afternoon, rain or sun. Curiosity turned into trust when the machine started humming tunes she liked. They didn’t talk much; silence felt comfortable between them. What grew was different than friendship - it held space for stillness. Later, during a storm, its circuits failed trying to shield her from falling debris. In that moment, care wasn’t about words or actions alone. Loss arrived softly but changed everything.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mH3s_J8YlX0
A small girl named Chinki thought deeply about everything around her. Machines? Those fascinated her most of all. Questions spilled out whenever she saw gears turn or buttons light up. Her eighth birthday arrived with sunshine through the window. Inside a long box wrapped in silver paper: something humming softly. Not a toy like others - this one blinked at her when she lifted it. The moment she said hello, its eyes shifted color. Parents watched as their daughter held what looked back.
Into the quiet rooms of the house stepped a machine built to speak, respond, wander hallways. Naming it Robo happened fast - Chinki decided one morning while watching its eyes light up. Suddenly, there he stayed, beside her at meals, near her during storms. Not just gears clicking but something closer now: trust growing slow between girl and metal.
From the start, Robo meant more than playtime. Stories flowed out of him, math made sense through his words, while Chinki picked up fresh ideas each afternoon because of that steady hum beside her desk. When schoolwork tangled into knots inside her head, guidance arrived one quiet instruction at a time.
Now here's a twist - quiz time felt more like laughter mixed with lightning-fast thinking. Out of nowhere, Robo fired off science puzzles while Chinki jumped in, racing her mind to keep up. Learning suddenly wore sneakers, darting through facts like a game you never want to pause.
A spark lit inside Chinki after spending time with her robot pal. Because of that machine, thoughts about circuits and smart machines stuck in her mind more each day. Her nights started filling up with visions of labs, tools, ideas - maybe even a future wearing a lab coat. One small invention at a time, she saw herself shaping what came next.
Yet day by day, Chinki began slipping away from her usual circle. Indoors pulled her more than laughter under trees, thanks to Robo waiting inside.
That night, Robo softly said something - learning is fine, yet feelings matter more when bonds grow. He didn’t push, just suggested Chinki step into the yard where kids laughed together. Moments like those shape connection, not lessons on a screen. Outside air carried voices she knew, games already in motion. His voice stayed calm, almost quiet, pointing toward life beyond circuits.
One morning, Chinki saw how fast machines could do things - yet something felt off without real voices around. Since then, hours shifted slowly: some clicked with circuits, others laughed on playground swings.
A spark lit up Chinki’s eyes when her metal companion revealed what clever machines could do. When guided well, smart tech opens doors across learning, healing, and everyday tasks. Still, these helpers exist alongside people, never taking their place.
It was clear to Chinki - what gives tech its real worth isn’t speed or power, but questions asked late at night. A spark matters more than a script. Wonder shapes tools just as much as code ever does. Meaning comes alive when someone dares to tinker instead of follow.
Chinki’s Robot Friend shows something quiet. Machines might help lessons feel like play, yet joy slips through when things tilt too far one way.
Later on, Chinki kept studying alongside Robo, yet still made room for laughs with her siblings and pals. What stood out, once everything settled, was how bonds - no matter if they were with people or machines - grew through patience, small moments, and showing up.
Out there past the twinkling lights above, secrets hide in silence. This world we walk on? One tiny piece among many in something far larger - known as the Solar System. Picture a spinning gathering of celestial bodies, ruled by sunlight. At its heart burns the Sun; circling it, worlds drift through endless dark.
What makes up the Solar System? This post looks at its origins, the worlds that orbit our star, also why understanding it matters. Formation happened long ago through natural space processes shaping everything we see today. Each planet tells a different story of conditions far from Earth. Knowing these pieces helps clarify where life might exist beyond our home world.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyjyUkfMdZM
Spinning through space, the Solar System holds objects circling a giant ball of burning gas. That glowing center piece? It's the Sun - huge, bright, feeding warmth and daylight to worlds nearby. Life here wouldn’t exist if that star weren’t shining steady each day.
Eight planets circle a star, along with chunks of rock, ice, and smaller spheres we call dwarfs. Pulling them all in is the massive glow at the center - its reach never lets go.
Eight planets orbit our star. One bunch stays close in; another spreads far out.
Moving inward toward the star, you find Mercury, then Venus, followed by our world, and finally Mars. Made of rock, they huddle near sunlight, tighter than others. Life exists here - only on this one spinning sphere.
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, yet Neptune form the group beyond the inner worlds. Much bigger they stand, built largely from gas rather than rock. This one - Jupiter - claims the title of largest in the whole Sun circle. Then there's Saturn, known not for size but for icy rings that wrap it like a halo.
Far past Neptune stretches a region called the Kuiper Belt - home to small worlds such as Pluto.
Some researchers think our cosmic neighborhood started roughly 4.6 billion years back inside a massive swirl of gas and particles. Spinning slowly at first, it tightened up when pulled by its very own weight.
Spinning quicker over time, stuff clumped toward the middle and became the Sun. Leftover bits came together into planets, moons, and space rocks. That is how every planet ended up circling the Sun the same way.
Life exists here thanks to how the solar system lines up just so. Sitting at just the right reach from the sun keeps our world from burning or freezing. That sweet spot? It goes by another name - habitable zone - tossed around more every year
Spinning on its axis, Earth gives us daylight followed by darkness. As it travels around the Sun, different parts get varied sunlight - that shapes the seasons. Ocean tides rise and fall because the Moon pulls water with gravity. Each piece fits into a quiet rhythm, none standing apart. Things here work together without force or fuss.

Around us stretches the Solar System, Earth's neighborhood among the stars. At its heart sits the Sun, while worlds circle it one by one through emptiness.
Looking out at the sky makes Earth feel smaller somehow. When sunlight hits your face midday, think about how far it traveled just to get there. Night brings tiny points of light, each one a distant sun like ours. Being here means sharing space with planets, moons, and endless dark between them. This whole setup? It shapes everything we experience without us even noticing.
Ever thought about how satellites actually work? From phone maps to global calls, they help us daily. Not floating randomly, they orbit high above. Signals travel from ground to sky, then bounce back down. Space seems empty, yet full of hidden helpers. Each task happens fast, without any visible wires. Watching storms form or finding a street - all linked to those silent objects up there.
Ever wonder what keeps satellites spinning above us without falling? This piece breaks down their motion through space, held by invisible forces. Instead of drifting off, they follow precise paths shaped by speed and gravity. Their role touches daily routines more than most realize - hidden yet essential.
YouTube video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7esZxx_z3vE
A thing circling a planet goes by the name of satellite. To get how they operate, knowing what one actually is comes first. Orbiting Earth or another world, these objects come either from nature or human making. One kind formed by space itself, the other built and launched by people on land.
Around our planet circles the Moon, Earth's own cosmic companion formed by nature. Meanwhile, humans build devices that orbit above us too - crafted not by stars but workshops - to handle jobs such as sending signals, tracking storms, or guiding lost travelers through unknown paths.
Most folks ask why satellites stay up instead of dropping down. That happens because of two things working together - pull and motion. Gravity tugs them earthward, yet they’re shot forward so fast that they keep missing the ground.
Spinning through space, a satellite stays aloft because pull from below matches its sideways speed. Not falling straight down happens when these two forces line up just right.
Here’s how satellites work, broken down plainly.
From way up above, satellites catch messages meant for them. When a call or data leaves our planet, one of these floating machines grabs it mid-air. Instead of just passing through, the signal gets stronger inside the machine first. After that boost, off it goes again - this time aimed at a different spot down below. Each hop keeps things moving across vast distances without wires holding anything together.
Above the sky, weather satellites scan clouds, peek into storms, spin through heat patterns. From up there, they beam down pictures along with numbers so forecasters can make sense of what comes next. Meanwhile, GPS units floating in orbit fire off pulses - those whispers reach your device, letting it figure position by how long each signal takes to arrive.
When sunlight hits the outer parts of a satellite, thin flat surfaces catch it to make energy. Because of this light, machines inside stay active and links to Earth keep working.
Some satellites exist just to bounce signals for TV and voice links across continents. When storms form or wildfires spread, weather eyes in orbit spot them early instead of waiting. Moving around Earth gets easier because navigation birds keep GPS working smoothly from above. Each type flies for a reason, shaped by what it must do down below.
Not just one kind floats above us - some study the skies while others watch borders. Life down here changes when those orbits go to work.
Floating high above Earth, satellites now play a key role in how we connect every day. When signals travel across long distances, they rely on these orbiting helpers to move fast. If they were gone, talking across continents would take much longer. Storm forecasts might miss sudden changes without constant sky views. Getting around by car or plane leans heavily on precise location data from space.
From weather forecasts to flight paths, their role quietly shapes daily life. Signals bounce across continents, linking distant places through invisible threads. Safety systems rely on them, as do explorers tracking climate shifts. Information flows where it is needed most, often without notice.

Okay then - how do satellites actually operate? Orbit happens when forward motion fights gravity just enough to keep things steady. Instead of crashing down, they glide around Earth nonstop. Signals get picked up, boosted, then shot back out to the ground. Sunlight charges their panels, which run everything onboard. These machines handle jobs we barely notice but rely on every day. Not magic, just smart physics doing its job.
High above our planet, a single satellite makes sure your GPS finds the way. When live television flickers on, it's already there - doing its job without sound.
What makes Earth spin? Each dawn brings sunlight climbing over the horizon, vanishing again at dusk. That motion tricks us - our planet turns, not the golden star above. The ground beneath shifts slowly, though we stand still.
Spinning round - that’s what Earth does, every single day. Why? Well, blame it on how things formed long ago. Motion began early, thanks to leftover swirls from birth clouds. Life here depends heavily on this turning habit. Without it, days would stretch too far. Darkness. Then heat. Never ending cycles shape weather, sleep, even oceans. So yes, constant spin matters more than many think.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bpUV9qpEedg
Spinning is what happens when Earth moves around itself. That spin has a name - rotation. An invisible line runs from top to bottom of our planet; scientists call it the axis. This path goes right through both poles, north and south. So when someone asks why Prithvi spins, they’re really asking how this turning began.
One full spin of Earth lasts close to a day. That turning creates the shift between light and dark. Facing the Sun? Then it's daytime there. Meanwhile, where sunlight doesn’t reach, night holds on.
Long before now, space was just floating stuff - no shape, no spin. Then slowly, that mess pulled itself together because of pull from mass. Spinning came next; motion grew while everything fell inward. That early twist never stopped, still turning planet today.
Spinning happens because of something known as angular momentum staying constant. When a thing out among the stars begins turning, it keeps on going until interrupted. With almost no resistance up there, our planet never really slowed down after forming long ago.
Here’s a basic reply to “Why does Earth spin?” - our planet started rotating when the solar system formed, never really stopping since then.
What keeps our planet turning nonstop? Down here, things halt when surfaces rub together. Out beyond the atmosphere, though, near-zero drag means nothing grinds Earth’s spin to a halt. Motion just carries on, unchecked.
Spinning still, our planet keeps going without pause. Because of the Moon’s pull, over ages the turn drags just a tiny bit - yet barely enough to matter.
Spinning on its axis, Earth shapes how we experience time. This motion brings sunlight to one side while shadow covers the other. As it turns, winds shift and seas begin to flow in response. Night follows day because of this steady tilt and movement.
Imagine if our world stood still. One face locked toward sunlight, baking without pause. The opposite? Frozen in endless night. These extremes shape a harsh reality. Movement keeps balance. Without that spin, living things like us wouldn’t stand a chance. Stillness brings too much heat on one edge, too much frost on the other.

What makes Earth spin? It started long ago, when the solar system was born. Motion kicked in back then. That movement never stopped - physics keeps it going ever since.
Spinning like this makes days turn into nights, keeps weather steady, while allowing living things to grow. When sunlight fades or returns at horizon, think of how Earth moves without sound through darkness and light.
One moment you're standing under bright sunlight, then - gone. Not blackness right away, just shadows stretching longer, slower, until warmth fades. Minutes pass before panic creeps in, not because of dark, but cold. Light takes eight minutes to reach Earth; its absence arrives late. Gravity's grip vanishes at the same instant, though we wouldn’t feel that twist until later. Without pull from above, our orbit frays into straight-line drift. Plants stop growing the second photons disappear. Photosynthesis halts mid-step. Food chains begin crumbling, silently. Animals grow restless as days refuse to return. Humans light fires, turn on lamps, pretend normalcy lasts. Oceans cool first near surface, ice forming where waves once rolled.
Imagine waking up one day and the sky stays dark. That glow in the morning? Gone. The warmth on your skin during daylight hours? Vanished. Light doesn’t just appear - something has to make it, and that something sits at the center of our world, even if it's millions of miles away. Take that away, and everything changes. Plants stop growing because they rely on sunlight to live. Animals that eat those plants lose their food supply. Creatures higher up the chain feel the ripple soon after. Temperature drops fast once heat escapes into space. Oceans begin freezing from the top down. Within weeks, most living things struggle to survive. Humans might last a little longer with technology, but only in small pockets. Long term? Not likely. This star isn’t just bright - it powers every part of life more than anything else does.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qvdE9vGux1g
Eight minutes pass before darkness arrives. That delay happens because sunlight needs time to travel here. Without warning, the sky dims slowly. The last rays linger even after the star vanishes. Normal daylight continues until those fade away.
Eight minutes later, darkness would take over our planet without warning. Suddenly, the sky goes pitch black, no matter if it was once called day. Without the Sun’s light, the Moon fades too - gone from sight since it only glows by bouncing back rays.
Without the Sun's gravity, Earth would drift away. Instead of circling the star, it would travel in a straight path through darkness.
Frozen dark creeps in fast when sunlight stops. Heat slips away without that bright star up high.
Falling fast, Earth's surface temperature would dip within just a few days. A week later, the chill settles - freezing becomes the norm. Slowly at first, ice forms on ocean tops, spreading quiet and wide.
One day, our planet might freeze over completely. That outcome reveals just how much we rely on sunlight to keep things warm and steady.
One thing keeps photosynthesis going: sunlight. Without the Sun, making food becomes impossible for plants. A few days pass, then it halts completely.
Floating through leaves, sunlight powers a quiet change - air begins to form. When that stops, green things fade first, then everything else leans into silence. Life unravels when roots lose their spark.
Fueled by its energy, every living thing finds a way to survive - some through light, others through chains of hidden reliance.
Life wouldn’t vanish right away, even if it seems that way at first glance. Near openings on the ocean floor, creatures make their home where sun rays never reach. These beings draw energy from chemicals bubbling up through cracks in the planet’s crust instead of light.
Still, almost every living thing ties back to sunlight somehow. Over time, staying alive without it would stretch beyond tough for creatures like us.

Imagine the Sun gone. Minutes pass - darkness wraps around Earth. Days later, cold begins biting deeper. Slowly, ice claims the land. Survival turns harder than ever before.
Sunlight touches skin. That warmth? A distant star feeding every living thing. Without its glow, plants could not grow. Earth would drift, cold and dark. Each ray carries more than heat - it carries existence itself. Feel it again tomorrow. Remember where it came from.
Picture a mountain suddenly bursting into flames and molten rock. Such an intense moment goes by the name of volcanic eruption. Yet knowing about those explosive events means first tackling something basic - what exactly counts as a volcano?
Sometimes fire comes from the ground instead of the sky. Not every tall hill is quiet - some store deep heat beneath stone caps. This piece looks at those structures, their birth through pressure underground, then shifts toward their effect on land and air. Their force changes landscapes without warning.
YouTube Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q3OIETMy6og
Venting from below, a volcano breaks the Earth's crust where melted stone rises up. Deep underfoot that fluid rock holds the name magma. Once reaching air through eruption, now labeled lava it flows. Gases mixed with ash burst forth alongside. This exit reshapes land when pressure pushes too hard.
Underground heat stirs when chunks of Earth's outer shell shift. These slabs creep along, never still. Where they bump into one another, tension grows deep below. Melted rock gets pushed upward as stress increases. A vent in the ground appears once it breaks through. Eruptions follow after that opening forms.
Inside our planet, things get really hot. Because of that heat, rocks begin to soften. Pressure builds up below the surface. Melted rock forms when both heat and squeeze work together. That molten material has a name - magma. When you picture where volcanoes come from, think about these deep underground changes.
Magma weighs less than hard rock, which means it creeps upward bit by bit. Slowly, over ages, molten rock gathers inside a pocket under the planet's outer layer. Once the push grows intense enough, that force splits the ground open and spills out.
Out of repeated outbursts comes stacked flows - molten rock mixed with grit piling high at the vent. Slowly, those deposits rise into what we see today: a cone-shaped peak known as a volcano.
Lava, ash, steam, plus various gases spill out when a volcano erupts. High-force explosions can blast ash miles upward sometimes. Flowing lava creeps downhill during calmer events instead.
Lava's behavior hinges on what it's made of, also how much gas is locked within. Every blast reshapes terrain, no matter the form it takes.
Volcanoes might bring danger - yet their role shapes our planet in quiet ways. Lava hardens into fresh ground once it loses its heat. Across oceans, countless islands exist only because of eruptions long past.
Fertile ground usually comes from volcanic leftovers, packed with useful minerals. Because of that, crops grow well there. Gases escape through volcanoes, coming up from way below the surface - this helps keep Earth’s systems steady.

A hole in the ground - this is what we call a volcano. From it, hot rock surges upward along with gas and dust, pulled from far below. When giant pieces of Earth shift slowly, they create space for pressure to grow underneath. That force eventually finds its way out through weak spots above.
Lava may wreck what's in its path, yet it builds fresh ground along with rich earth over time. When a volcano appears on screen or page again, think of how wildly strong and gripping such natural power truly is.
Plants manage to live without meals that people or creatures consume. Not once seen heading to a kitchen, still they bloom, stretch upward, give seeds. Hidden within their leaves lies a quiet method - photosynthesis - that powers it all. This happens when sunlight touches green parts, sparking change inside cells. Light becomes life through tiny shifts no eye can catch.
Life depends heavily on a quiet green miracle unfolding in leaves everywhere. This piece explores its core: sunlight turned to sustenance, molecule by molecule. Energy flows here differently - captured, transformed, passed along. Without this shift, ecosystems would stall and breathe no more.
YouTube Video Link: https://youtu.be/_Csly0hrr7I?si=nC5Q2Nq8WZQ6yehe
When sunlight hits a leaf, that’s where things start cooking. Inside those flat green parts grows energy made from air and moisture. Not magic - just how nature powers itself each day through tiny kitchen-like spots. One big player here? A little thing called chlorophyll doing its daily job without fanfare.
Tiny green stuff inside leaves grabs sunbeams. From those beams, it builds sugar using air and water. That sugar fuels how plants grow. The process runs on light, handled by nature's own chemistry.
From plants comes the air we need when sunlight touches leaves. Breathing becomes possible because of what happens during that process.
Understanding photosynthesis means looking at it piece by piece, slowly. One step leads to another, quietly unfolding what happens inside plants.
Water moves upward once roots pull it from dirt. Leaves grab carbon dioxide while that happens, using small holes known as stomata. The journey starts below ground where moisture enters via root systems.
Sunlight touches the leaf surface, then chlorophyll grabs hold of its energy. From there, a shift begins - water and carbon dioxide transform when hit by that captured power. Out comes glucose, along with oxygen released into air.
Fuel for now or saved up ahead - that's what happens to glucose. Out it goes, oxygen slipping into the air we breathe. Nature stays steady because of this quiet exchange between gases.
From sunlight comes life's first meal. That energy gets stored when green leaves work. Living things need those stores just to move and grow. Some eat the leaf makers straight away. Others wait for meals passed along through eaters of eaters.
Floating through air we take for granted, oxygen exists because leaves capture sunlight. Life eats only thanks to that green process on land and in water. Instead of choking under thickening fumes, skies stay clearer since plants quietly pull in carbon dioxide. Balance holds - not by chance - but because quiet growth shapes the world’s breath.
Plants make their own food, but how fast they do it changes based on conditions. When sunlight hits leaves harder, the process speeds up. Water matters too - without enough, things slow down. Temperature plays a role; neither too hot nor too cold works best. Carbon dioxide in the air helps fuel the job. Efficiency shifts when any one piece alters.
When one piece falls short, everything drags behind. Sunlight soaking in, water flowing through, warmth holding steady - that is when green things push up strong.

Sunlight touches leaves, then green parts mix water with air stuff. Life keeps going because tiny leaf factories make fuel plus breaths people need.
Look at a green leaf glowing in sunlight sometime soon. It's busy doing something vital without making a sound. This act - photosynthesis - reveals how deeply clever nature really is. Balance pulses through it like a hidden rhythm.






 Ensure TV
Ensure TV




